How Many Brake Sensors Does A Car Have? Inside Your Car’s Braking System
Modern cars can be confusing, especially their safety systems. A crucial but overlooked part is brake sensors – how many does a typical car have? Understanding subtle but vital components like sensors is key to truly grasping how vehicles function.
The challenge lies in the variety of car models. While a precise number would be convenient, it varies. Most cars have 4-6 brake sensors, but factors like size, brake complexity, and safety rules influence the count.
I’ve been trying to understand how brake sensors work in cars to keep us safe. It’s interesting to see how important they are for a car’s performance and safety. The more I learn, the more I realize their significance.
For those curious about brake sensors, let’s explore their role in car safety. Join me to uncover how they help with maintenance, giving all drivers a clear understanding.
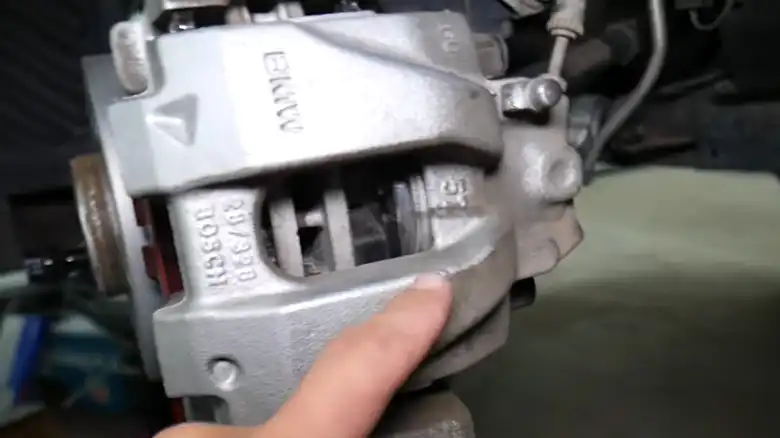

Brake Sensors a Car Have
Discover the number of brake sensors in your car. Learn how these crucial components contribute to safety and performance, ensuring a smooth and secure driving experience.
Total Count
Adding Up the Sensors: To determine how many brake sensors your car has, add up the sensors from each category. Typically, this will result in four to six sensors, but it can vary based on your vehicle’s make and model.
Variations in Sensor Count Among Car Models: The exact number of brake sensors can vary based on your vehicle’s size, brake system complexity, and adherence to specific safety standards and regulations.
Factors Influencing Sensor Count
Vehicle Size: Larger vehicles may have more sensors due to their increased weight and braking demands. Smaller vehicles may have fewer sensors.
Brake System Complexity: Vehicles with advanced braking systems may require more sensors to ensure optimal performance.
Safety Standards and Regulations: Different regions and countries may have specific safety standards that affect sensor requirements.
Types of Brake Sensors
Brake sensors come in several varieties, each designed for a specific purpose. The primary types of brake sensors in a car include:
Brake Pad Wear Sensors: These sensors monitor the condition of your brake pads and alert you when they are worn down, signaling the need for replacement.
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) Sensors: ABS sensors play a critical role in preventing wheel lockup during sudden braking, enhancing your vehicle’s stability and control.
Traction Control System Sensors: Traction control sensors work to maintain traction by detecting wheel spin and adjusting power delivery to the wheels.
Brake Pad Wear Sensors
Explaining the Purpose: Brake pad wear sensors are your first line of defense when it comes to brake maintenance. They detect when your brake pads have worn down to a certain point and trigger a warning light on your dashboard.
Location and Functionality: These sensors are typically located near the brake pads, where they can monitor the thickness of the friction material. When the material becomes too thin, the sensor triggers the warning system.
How Many Are Typically Installed?
Most vehicles come equipped with two brake pad wear sensors, one for the front brake pads and one for the rear. This dual setup ensures comprehensive monitoring of your brake system.
ABS Sensors
What They Do: ABS sensors are integral to your vehicle’s anti-lock braking system, which prevents wheel lockup during emergency braking. These sensors monitor wheel speed and transmit data to the ABS control module.
Number of ABS Sensors in a Car: The number of ABS sensors in a car corresponds to the number of wheels. Most cars have four ABS sensors – one for each wheel – but some larger vehicles may have more.
Role in Preventing Wheel Lockup: The data from ABS sensors allows the system to modulate brake pressure, preventing wheel lockup and maintaining steering control.
Traction Control System Sensors
Defining Traction Control: Traction control is a feature that enhances stability by reducing wheel spin during acceleration. Traction control system sensors play a pivotal role in this process.
Sensor Functionality in Traction Control: Traction control sensors monitor wheel spin and adjust the power delivered to the wheels to maintain traction on slippery or uneven surfaces.
How Many Sensors Are Typically Employed?
Most cars equipped with traction control have a sensor on each driven wheel, typically two in total, to effectively control traction.
Why Multiple Sensors?
Explore the reasons behind the presence of multiple brake sensors in your car. Discover how redundancy and precision enhance safety and reliability on the road.
Enhancing Safety
Redundancy for Reliability: Multiple sensors offer redundancy. If one sensor fails, others can still provide crucial data for safe braking.
Improved Braking Performance: Multiple sensors contribute to better braking performance, especially in emergency situations.
Diagnostic Capabilities
Identifying Specific Issues: Having multiple sensors allows for a more precise diagnosis of brake system issues, enhancing overall vehicle safety.
Alerting the Driver: When an issue is detected, the sensors can quickly alert the driver, preventing potential accidents.
Brake Sensors’ Role in Modern Cars
Learn about the critical functions of brake sensors in today’s vehicles. These sensors are at the forefront of safety and performance, ensuring a smooth and secure driving experience.
Safety Advancements
Emergency Brake Assist: Brake sensors play a pivotal role in emergency brake assist systems, ensuring that the car can stop quickly and safely in a critical situation.
Adaptive Cruise Control: These sensors also contribute to the functionality of adaptive cruise control systems, maintaining a safe following distance from the vehicle in front.
Maintenance Benefits
Cost-Efficient Repairs: Brake sensors help prevent unnecessary brake component replacements, saving you money in the long run.
Extending Brake Component Lifespan: By alerting you to worn brake pads early, these sensors help extend the lifespan of your brake components.
Common Issues with Brake Sensors
Explore the typical problems that can arise with brake sensors. Understanding these issues is essential for maintaining your car’s safety and performance.
Sensor Malfunctions
Signs of Sensor Failure: Signs of sensor failure can include a warning light on your dashboard, which should not be ignored. It’s important to diagnose and address the issue promptly.
Diagnostic Procedures: A diagnostic scan can determine which sensor is malfunctioning, helping you pinpoint and replace the faulty sensor.
Maintenance and Replacement
Brake Sensor Replacement: Replacing a brake sensor is a relatively straightforward process. However, it’s essential to consult your vehicle’s service manual or seek professional help if you’re not confident in your DIY skills.
DIY vs. Professional Service: If you’re experienced in vehicle maintenance, you can replace a brake sensor yourself. But for those less familiar with car repair, it’s wise to rely on a professional mechanic.
Queries and Solutions
Q1. What do ABS sensors do, and how many are there in a car?
A: ABS sensors monitor wheel speed and prevent wheel lockup during braking. Most cars have four ABS sensors – one for each wheel.
Q2. Can I replace brake sensors myself, or should I seek professional help?
A: Brake sensor replacement is possible for DIY enthusiasts, but professional help is recommended for those unfamiliar with car repairs.
Q3. Do all cars have traction control system sensors, and how do they work?
A: Not all cars have traction control, but those that do typically have two sensors, one on each driven wheel. These sensors monitor wheel spin and help maintain traction.
Q4. How often should I check my brake sensors for wear and tear?
A: It’s a good practice to check your brake sensors during routine maintenance, such as when changing your brake pads or having your brakes inspected.
Bottom Line
Perception how many brake sensors a car has is important for both safety and maintenance. These sensors are the unsung heroes of your vehicle’s braking system, constantly working to ensure your safety on the road. By comprehending their roles and why multiple sensors are employed, you can drive with confidence, knowing your brakes are in optimal condition.



![[Answered] Does Cruise Control Drain Battery?](https://proautosafety.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Does-Cruise-Control-Drain-Battery-768x431.webp)
![[Explore] Can You Use LED Fog Lights as Headlights?](https://proautosafety.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Can-You-Use-LED-Fog-Lights-as-Headlights-768x431.webp)